C-NPT: Pulmonary
Quiz Summary
0 of 43 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 43 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- Medical 0%
- Resuscitation 0%
- Special Populations 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 43
1. Question
A 12-kilogram child sustained a salt-water drowning and aspirated approximately 250 mL of fluid. Which of the following would NOT be a concern for potential problems?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 43
2. Question
A 12-year-old diagnosed with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is being transported. They are 5’0” and weigh 56kg. While in the ED, they have been breathing at a rate of 38 breaths per minute, and they appear fatigued. The decision to made to intubate the patient and current ABGs are requested. They are as follows: pH 7.01, PaCO2 23, PaO2 280, HCO3– 17. They are currently on a non-rebreather (NRB) at 15LPM. Which of the following plans would best suit this patient initially?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 43
3. Question
A 30-week gestation, 1.5kg, neonate delivered three hours prior is being transferred. The most recent chest x-ray demonstrates a ground glass appearance. Current vent settings: SIMV 26, PRVC, Vte 8, f 48, FiO2 0.21 and PEEP 5. Current ABG: pH 7.24, PaCO2 38, PaO2 40, HCO3– 24. What condition do you suspect?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 43
4. Question
A 32-week premature neonate is experiencing respiratory distress. Which drug may be administered in preparation for transport?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 43
5. Question
A 4-year-old with a past medical history of asthma is in respiratory distress and appearing anxious. Current vitals: BP 80/32, HR 130, RR 38. Crackles are auscultated throughout the lungs. The patient is placed on the monitor, and sinus tachycardia is noted. Upon review of current arterial blood gas results, you would anticipate which of the following findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 43
6. Question
A 48-week post-conceptual age infant with a respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is being transported. This infant is at increased risk of which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 43
7. Question
A child aspirated a coin, and their left lung is hyperinflated. Where is the coin?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 43
8. Question
A patient has a SpO2 of 87%. What would the associated PaO2 be?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 43
9. Question
A patient with a tension pneumothorax is best treated by needle decompression at the following site:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 43
10. Question
A patient being transported presents with minimal air movement despite having received two nebulized breathing treatments of albuterol and ipratropium. The next action for this patient will be:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 43
11. Question
A pediatric status asthmaticus is being transferred. What finding indicates impending respiratory arrest?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 43
12. Question
A soft tissue neck x-ray reveals a “steeple sign.” What is the underlying concern for this finding?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 43
13. Question
Acute respiratory failure is defined as what?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 43
14. Question
For an infant with a respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), the best treatment combination is which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 43
15. Question
Identify the following chest x-ray of a 4-day-old infant presenting with decompensation:
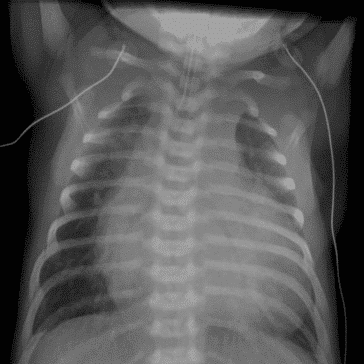 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 43
16. Question
Identify the following chest x-ray of a premature infant:
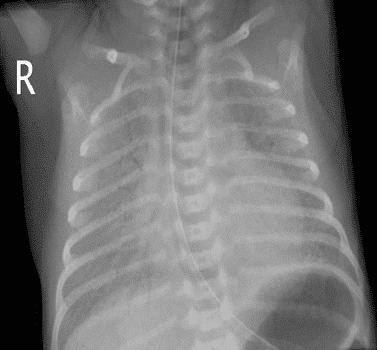 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 43
17. Question
Identify the following chest x-ray:
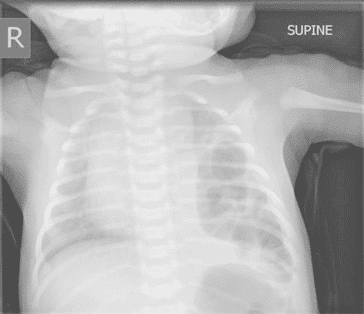 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 43
18. Question
Identify the following chest x-ray:
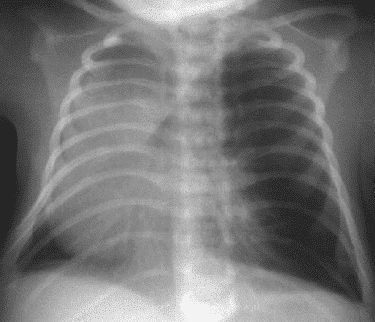 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 43
19. Question
Identify the following x-ray:
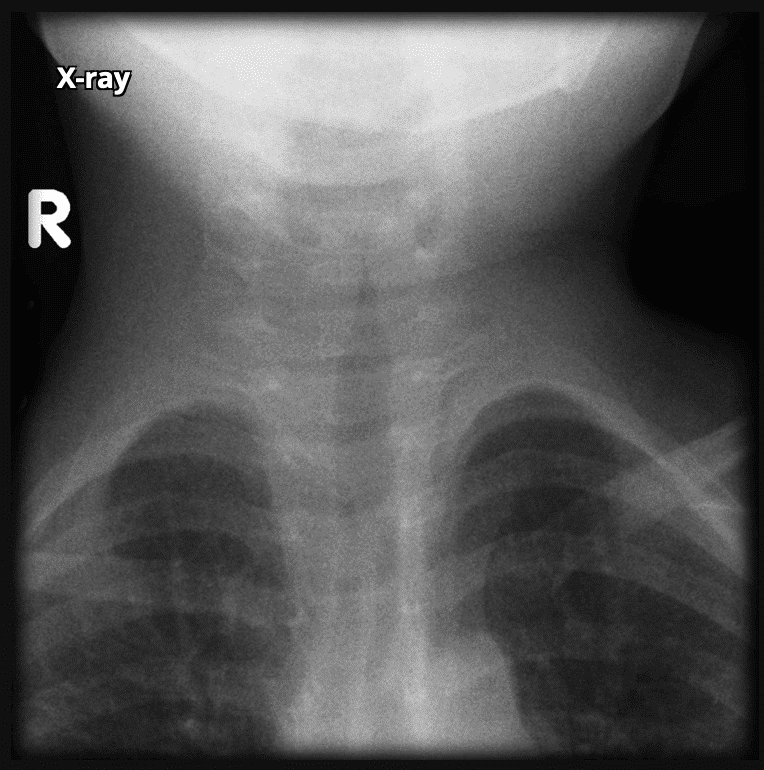 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 43
20. Question
Identify the following x-ray:
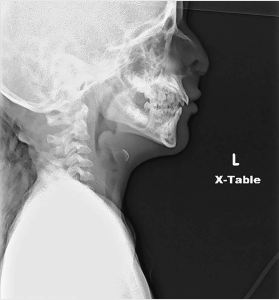 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 43
21. Question
In a patient experiencing status asthmaticus, all of the following are expected findings EXCEPT for?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 43
22. Question
Indications for intubation of the asthmatic patient include which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 43
23. Question
Oxygen delivery (DO2) is a product of what?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 43
24. Question
The proper depth of a 3.5 endotracheal tube (ETT) would be?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 43
25. Question
The purpose of a trachea hook during a surgical cricothyroidotomy is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 43
26. Question
The team is caring for a 60-kilogram ideal body weight (IBW) patient on a ventilator. The patient is receiving a 300 mL tidal volume. The exhaled tidal volume is 285 mL. These settings and observations:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 43
27. Question
What is a standard central venous oxygen concentration (SvO2)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 43
28. Question
What is the appropriate depth of insertion for a 5.0 endotracheal tube (ETT)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 43
29. Question
What is the appropriate un-cuffed endotracheal tube (ETT) size for a 4-year-old-patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 43
30. Question
What is the MOST appropriate I:E ratio setting for an asthmatic pediatric patient intubated for respiratory failure?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 43
31. Question
When administering Albuterol to a 4-year-old, which of the following changes would NOT be anticipated with the administration?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 43
32. Question
When evaluating a patient in acute respiratory failure, identify the most common finding.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 43
33. Question
When giving a neonate prostaglandin (PGE1), a potential complication to administration is?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 43
34. Question
When pre-oxygenating a 4-year-old rapid sequence intubation (RSI) patient, the strategy for doing so is?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 43
35. Question
Which medication causes a decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 43
36. Question
Which medication is recommended for sedation in a patient with asthma?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 43
37. Question
Which of the following can be associated with a poor prognosis in a patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 43
38. Question
Which of the following does not have bronchodilation effects?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 43
39. Question
Which type of cricothyrotomy is best performed in children that are less than eight years old?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 43
40. Question
You are transporting a 5 kg, 3-day-old neonate in severe sepsis and metabolic acidosis who is intubated and sedated. Before intubation, the patient’s initial respiratory rate was 44, with a corresponding EtCO2 of 22. What would be the most appropriate vent setting for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 43
41. Question
You are treating two pediatric victims of a house fire. The patients are exhibiting increasing signs of respiratory distress and cough after high-flow O2 is applied. What could be causing the patient’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 43
42. Question
You perform a needle thoracostomy on your neonate with a suspected “air leak.” After re-evaluating the neonate, which of the following would indicate that initial treatment was NOT successful?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 43
43. Question
Your patient is the victim of a near-drowning incident that occurred earlier today. They presented to the ED complaining of increasing shortness of breath. Upon assessment, they were found to be breathing at a rate of 42/min and crackles were auscultated in bilateral lower lobes as well as wheezing throughout the lungs. They were immediately placed on a non-rebreather (NRB), and ABGs obtained. Initial ABGs showed the following: pH 7.32, PaCO2 48 mmHg, PaO2 46 mmHg, and HCO3– 20 mEq/L. What is the next best action?
CorrectIncorrect
