Life Link III: New Hire Exam

Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
A patient has just been intubated for respiratory distress after blunt trauma related to an ATV vs tree collision. His EtCO2 is 38 mmHg and oxygen saturations 94% on 100% FiO2. The breath sounds are diminished on the left with positive gastric sounds in the left chest. The next priority is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
The most reliable objective method for verification of placement of a tracheal tube during transport is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
Immediately after intubation of a hemodynamically unstable patient the EtCO2 reading is 2 mmHg. The clinician recognizes the best explanation of this is that:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
An elderly female trips and falls from a standing position to concrete. She has a GCS 13, moves all extremities with a C- collar in place. Vital signs are a blood pressure of 130/80, heart rate of 60, and respiratory rate of 10. During your assessment she becomes apneic. The next most appropriate step is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
A construction worker has a diagnosed C4 injury in the ED. During your assessment, you note his GCS is 14 with no movement of extremities and no feeling below the nipple line. His blood pressure is 93/60, HR 80, respiratory rate 28, oxygen saturation 100% on 2 liters by nasal cannula, and EtCO2 70 mmHg. The clinician recognizes the next MOST appropriate action is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
A 28-week gestation female complains of severe headache and blurred vision. The patient’s vital signs are BP 160/110, HR 76, and RR 20. During your assessment, the patient develops a generalized seizure. Which medication is indicated first in this situation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
An adult female patient who was involved in an MVC is in an emergency department. The patient is supine on a long backboard with a cervical collar in place. Her current vital signs are BP 78/42, HR 128, and RR 24. The patient responds to loud verbal stimuli and is confused. Your physical exam reveals no external hemorrhage or major injuries. The patient has a visibly gravid abdomen. Your first intervention is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
The normal pH range for arterial blood is?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
An adult male patient presents to a hospital with anxiety, confusion, diaphoresis, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and hypersalivation. He developed these symptoms while working in an orchard. His vital signs are BP 140/90, HR 58, and RR 20. Which of these medications would you administer first?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
An adult patient who was diagnosed with DKA is being transferred to higher level of care. The patient is intubated and mechanically ventilated at 12 breaths per minute with 400 mL of tidal volume. The most recent arterial blood gas results are pH 7.0, PaCO2 36, PaO2 72, and HCO3 10. The most appropriate next intervention is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
The management of a patient experiencing an acute hemorrhagic stroke includes which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
The two main physiologic changes that cause shock in the septic patient are
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
Upon arrival at a remote hospital, you are presented with a patient who suffered facial burns 26 hours previously. He is experiencing respiratory distress and you are requested to intubate the patient prior to transport. Which of the following medications used for rapid sequence induction should be avoided on this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
Which of the following would be appropriate personal protective equipment for providers during transport of a patient with high fever, respiratory distress, hypoxia, and frequent cough?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
A 56-year-old male patient complains of substernal chest pain. The 12-lead ECG was diagnostic for an anterior STEMI. The patient’s vital signs are BP 138/86, HR 68, RR 14, and he currently rates his pain at 8/10. The patient was placed on oxygen and received Aspirin and SL Nitroglycerin. Which of these medications would be contraindicated in this situation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
A 58-year-old patient presents with weakness, respiratory failure, decreased level of consciousness, hypotension, and wide complex bradycardia. The patient has a history of end-stage chronic renal failure. Based on this information you know that the patient may require the administration of:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
A patient is receiving antibiotics. They develop a rash on their trunk and develop inspiratory and expiratory wheezing. The next most appropriate action is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
An adult trauma victim is being transported from a local hospital to a Level I trauma center. The patient is receiving the second unit of 0 negative packed red blood cells. During the transport, the patient begins experiencing itching, hives, and chills. The NEXT step is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
Management of a patient with a descending aortic dissection that has not ruptured would most likely include which of the following drug therapies?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
The best measure of adequate fluid resuscitation in a 2-year-old would be:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
You administer sublingual nitroglycerin to a patient for chest pain. What would indicate the need for further intervention during transport?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
You are about to administer hypertonic saline to a pediatric patient who weighs 30 kg. The order states to administer 5 ml/kg over 15 minutes. You program the infusion pump to deliver:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
During the assessment of your patient, they develop the following rhythm. Interpret this rhythm strip.
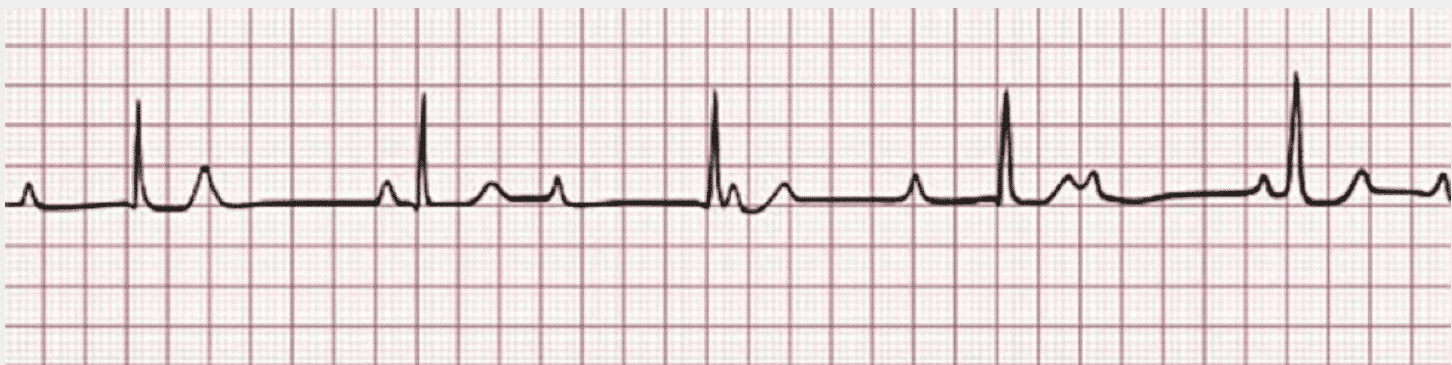 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
You just performed a 12-lead ECG on a 60-year-old female patient with complaints of severe weakness who experienced a syncopal episode earlier today. The ECG is shown below. What is your interpretation of it?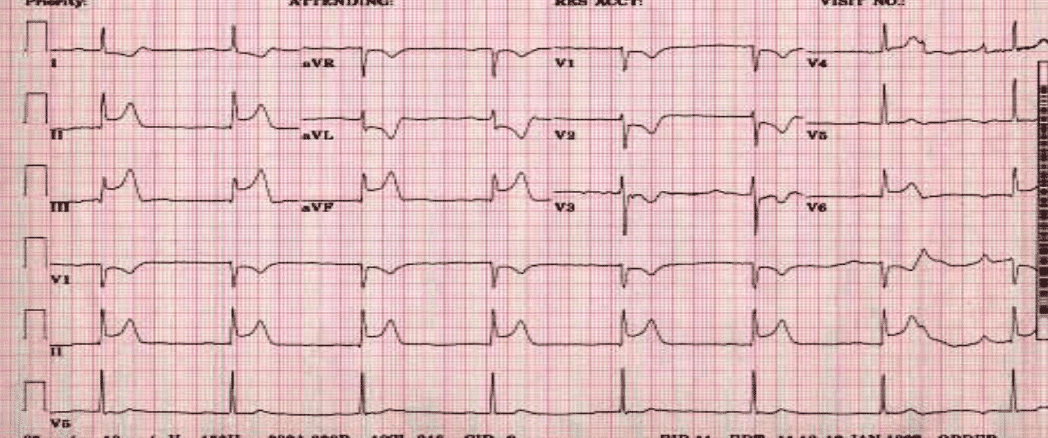 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
A young female is diagnosed with a massive pulmonary embolism. Physical assessment reveals pale, cool, diaphoretic extremities, and chest pain on inspiration. Vital signs blood pressure 70/30, heart rate 128, respiratory rate 36. The next MOST appropriate action is to?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
An adult patient arrives in the ED with a confirmed acute inferior wall MI. The vital signs include blood pressure is 82/50, heart rate 110, and respiratory rate 24 with oxygen saturations of 98%. The clinician anticipates the next most appropriate actions is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
A recently intubated adult, head injury patient is in the ED awaiting transfer. The patient was sedated and paralyzed 30 minutes ago with midazolam (Versed), and rocuronium (Zemuron). During your care the patient’s blood pressure changes from 130/70 to 170/100 and heart rate from 75 to 110. What is the MOST appropriate next intervention?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
During the pre-hospital phase of a traumatic brain injury (TBI), which two conditions reduce survival of this patient population?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
A pregnant patient (34 weeks gestation) is complaining of severe abdominal pain and loss of fetal movement. She describes the pain as sudden and severe in her abdomen. Assessment reveals that the patient is alert, anxious, with a pulse rate of 120, a blood pressure of 124/98, and cool and clammy skin. The patient has heavy, dark vaginal bleeding. The MOST likely diagnosis is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
A 2-year-old child has been diagnosed with decompensated hypovolemic. Which of the following solutions and volumes would you choose to administer initially?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
A two-year-old child is brought into the emergency department by his parents. They report that the child is not breathing normally. A quick assessment reveals an unresponsive child with agonal breathing, cyanosis, and weak, slow central pulses. Heart rate is 45. Your initial action should be:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
An initial assessment of a newborn infant following warming, drying, and stimulation, reveals peripheral cyanosis, a pulse of 80 bpm, flexed arms and legs with minimal response to stimulation, and no cry. The most appropriate next intervention is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
Which of these drugs is known primarily to lower afterload or systemic vascular resistance?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
Which of these drugs’ primary action is to improve cardiac contractility?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
A late sign of increased intracranial pressure (ICP) involves which changes?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
A motorcyclist hits a cow at a high rate of speed on a country road. The patient is unresponsive and intubated upon your arrival at the scene. His breath sounds are clear bilaterally with no JVD. After two liters of isotonic fluid for a blood pressure of 80/50, the current vital signs are BP 84/58, HR 128, oxygen saturations 96%, EtCO2 32 mmHg, RR 16 assisted by BVM. The next most appropriate action is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
A patient with a femur fracture and possible pelvic fracture is being prepared by you and your partner for transport. The patient has received 3 L of crystalloid solution, 1 unit of packed red blood cells, and 1 unit of FFP. The clinicians should focus their initial efforts on:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
On the scene is a patient with a stab wound to the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. The blood pressure is 88/50, HR 104, RR 22 with oxygen saturations of 94% on high flow supplemental oxygen. The next most appropriate action is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
A protester is hit with a can of soup in the left temporal area. The patient was initially found unresponsive and is now alert and oriented, complaining of a headache. During transport, the patient’s level of consciousness begins to deteriorate. The clinician expects the patient to have which type of condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
An adult victim was extricated from a burning building. The patient sustained a flash burn to the upper chest and face in a dryer explosion. The most concerning assessment findings in this patient would be:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
Assessment of a patient with a blunt injury to the right chest reveals hypoxia, jugular vein distention, subcutaneous emphysema, and a decrease in blood pressure. The most appropriate action is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
During the transport of a patient suffering from compartment syndrome in a lower extremity following isolated trauma, you note a complete absence of distal circulation in the extremity. You consult a physician’s medical direction who states the patient needs an emergency fasciotomy. You have received no training on this procedure. The most appropriate action is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
A 17-year-old was struck by a baseball in the left temporal area. He sustained a depressed skull fracture and developed a left fixed gaze with a fixed and dilated pupil on the left, and a 3mm reactive to the light pupil on the right. Vital signs are a blood pressure 190/110, heart rate 52, respiratory rate irregular pattern with the rate of 24 per minute. The patient is unconscious. The clinician recognizes this is consistent with:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
A young male has a penetrating wound in the right upper chest near the armpit. His vital signs are blood pressure 80/50, heart rate 104, respiratory rate 36, and oxygen saturation of 80%. The patient is restless with distended neck veins on physical exam. The clinician recognizes the patient MOST likely has a
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
An anxious adult patient arrives in the ED with vital signs of a blood pressure 64/48, pulse 130, respirations 28, temperature 97.1° F, and pulse oximetry of 94%. Physical exam revealed muffled heart sounds and the presence of jugular venous distension (JVD). The patient is one week post coronary bypass graph (CABG) x 5. The clinician recognizes the patient MOST likely has a:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
An intubated and mechanically ventilated trauma patient is being flown by your team from a small community hospital to a large tertiary center. Several minutes into the flight you note that the patient’s pulse oximetry decreased suddenly, a high-pressure alarm appeared on the ventilator, and the left side of the patient’s chest is not moving with each breath. Your immediate action is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
The oxygen saturation reading on an intubated, mechanically ventilated patient is 88%. To improve the oxygenation in this patient, the next step would be to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
When ventilating a pediatric patient in respiratory failure due to asthma exacerbation, the ventilation strategy should include which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
Which of the following statements regarding positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) is true?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
A patient is being mechanically ventilated. The MD states that he would like to improve ventilation. The clinician expects to adjust which values?
CorrectIncorrect
