APEx Neurological
Quiz Summary
0 of 30 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 30 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- Medical 0%
- Special Populations 0%
- Trauma/Burn 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
Diffuse axonal injury (DAI) will most likely represent how on a CT scan?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
The patient suffering from Brown-Sequard syndrome presents with what?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
A 15-year-old has a diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) secondary to a previously undiagnosed arteriovenous malformation (AVM). What is the systolic blood pressure goal for this patient during transport?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
A basilar skull fracture is associated with all of the following EXCEPT:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
A patient has an intracranial pressure of 28, and blood pressure of 100/60. Their cerebral perfusion pressure is approximately what?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
A patient has been involved in a traumatic fall from 30’, with associated upper extremity weakness, but not lower. What type of spinal cord injury is suspected?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
A patient has paralysis from the nipple line down. What vertebrae and dermatome are affected?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
A patient sustained significant trauma after a motor vehicle collision. They were initially unresponsive and demonstrated increasing respiratory difficulty and were intubated. Before intubation, their BP was 116/70 and HR 98. They respond to painful stimuli with decorticate posturing on the right side. Reassessment after intubation shows a BP of 170/52 and HR 60. What do you suspect?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
A patient was involved in a motor vehicle collision and sustained a severe head injury. They present with dilated and fixed pupils. This presentation occurs from increasing pressure on which cranial nerve (CN)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
A patient with a suspected spinal cord injury at C3 has stopped breathing. Which nerve has been affected?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
A pediatric patient is presenting with clinical signs of a spinal cord injury after a diving accident. They have no lower extremity movement; however, they can flex their arms but not extend them. Where is the fracture?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
A target adult cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) in a TBI patient should be at least?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
A 40-year-old male patient with a history of a traumatic brain injury is being transported by helicopter to a regional facility. During the flight, you review the medical records and note that the patient presented to the emergency department that morning with low serum osmolality, hyponatremia, and a high urine specific gravity. You suspect this patient may be suffering from:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
Calculate the cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) with the following findings: BP 150/75, HR 140, RR 28, SpO2 100%, CVP 2, ICP 25.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
Calculate the cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) with the following findings: BP 90/60, HR 110, RR 22, SpO2 98%, ICP 29, CVP 20, PA 32/14, PCWP 15.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
Cushing’s triad consists of which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
Identify and diagnose the following CT scan.
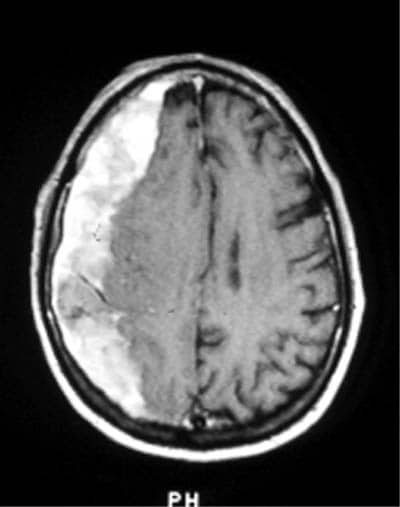 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
Identify and diagnose the following CT scan.
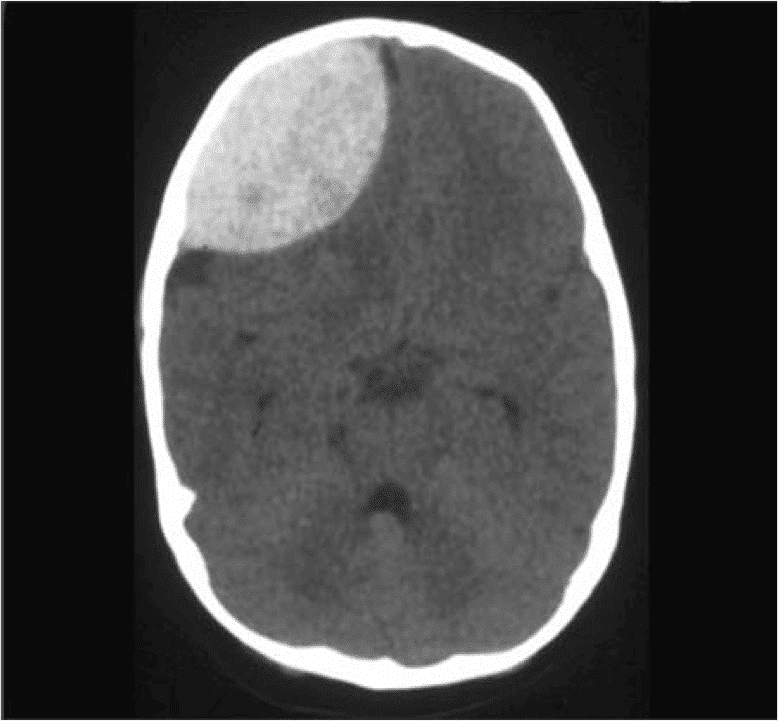 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
Identify and diagnose the following CT scan.
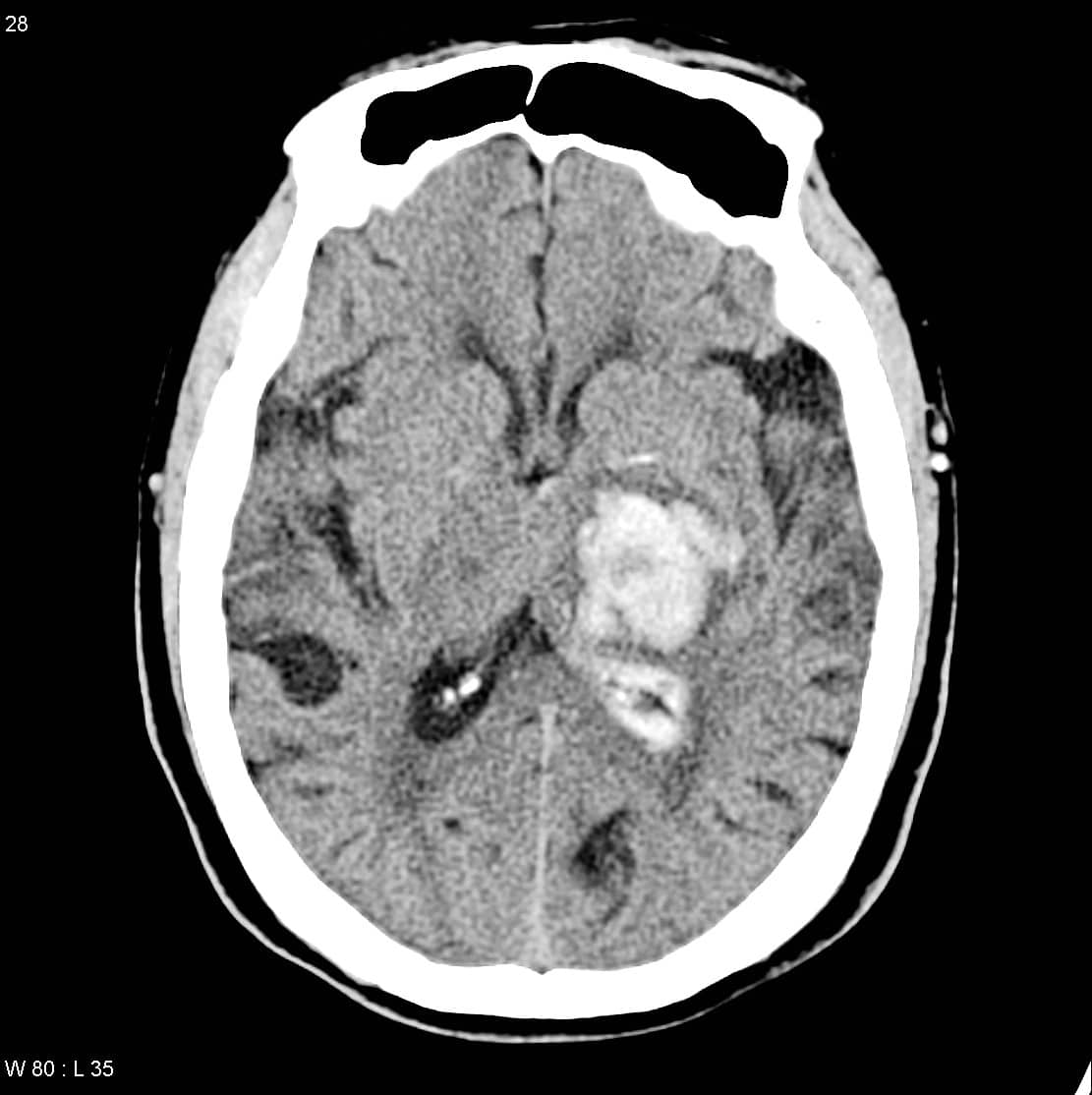 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
Identify and diagnose the following CT scan.
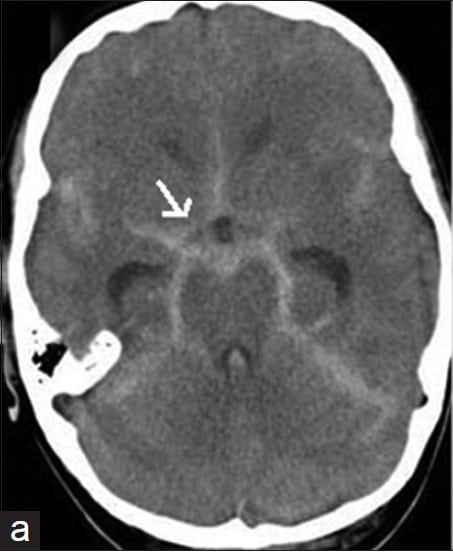 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
Spinal cord injuries that cause respiratory and diaphragmatic paralysis would be at what level?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
Tearing and bleeding of the cerebral veins that connect the subarachnoid space to the dural sinus is likely to cause a?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
The classic description of a patient suffering from an epidural hematoma is?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
To preserve brain function, a traumatic brain injury patient who is presenting in status epilepticus is best treated, initially, with:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
When monitoring invasive intracranial pressure lines, the transducer should be leveled where?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
Which type of head bleed has middle meningeal artery involvement?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 30
27. Question
You and your partner respond to a 10-year-old that fell at school. On arrival, the patient has an altered level of consciousness. EMS states that they had a brief loss of consciousness and a period of lucidness before the current decline in GCS. This presentation most often presents with what type of head trauma?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
You arrive on the scene to manage a fall victim. Current vitals: BP 70 by palpation, HR 60, RR 28, SpO2 96%. EMS reports the patient had a brief loss of consciousness but is now answering questions and conversing with a GCS of 14. You note a visible deformity to the right femur, and they are complaining of neck pain. What is your diagnosis of the patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
You respond to transfer a patient with a diagnosis of a skull fracture that is described as multiple fractures that radiate from a compressed area. What type of skull fracture does this patient have?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
The transport team provider has arrived to transfer a patient with a confirmed hemorrhagic stroke. During pupillary assessment the clinical provider notices bilateral eyelid retraction. What is this assessment finding called?
CorrectIncorrect
