APEx General Medical
Quiz Summary
0 of 98 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 98 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- Medical 0%
- Trauma/Burn 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 98
1. Question
A patient presents in a thyroid storm from an exacerbation of hyperthyroidism. What are their expected labs?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 98
2. Question
The patient has been diagnosed with acute myocardial infarction. They are complaining of increasing chest pain and difficulty breathing. They appear very nervous, and there is noted tremors. The ECG shows atrial fibrillation at a rate of 148. This patient may be experiencing:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 98
3. Question
Regarding the diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) patient, glucose should be decreased based on the following protocol?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 98
4. Question
A patient is receiving heparin after being diagnosed with a pulmonary embolus. After five days, they have developed heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. What clinical sign is expected initially?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 98
5. Question
Which of the following is associated with a poor prognosis in a patient with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 98
6. Question
A 12-year-old patient has a current pH of 7.52. Their previous pH was 7.41, and their potassium (K+) was 4.7 mEq/L. The expected current K+ is approximately what?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 98
7. Question
A 13-year-old patient has a history of insulin-dependent diabetes and recently admitted to a local ICU. The family states that they have had a cold over the past week and have become more lethargic over the last 24 hours. Lab results are as follows: Na+ 150, Cl– 103, glucose 504, WBC 12.3, bands 14%, leukocytes represent 68%. The most likely cause of this patient’s DKA state is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 98
8. Question
A 14-year-old patient is currently being treated for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). There is a noted decrease in mental status with associated lethargy, and their Glasgow coma scale (GCS) score is now 7, dropping from the previous 14. The neurological changes would most likely indicate which situation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 98
9. Question
A 15-year-old with a past medical history of diabetes mellitus presents very lethargic and only responsive to painful stimuli. They have been sick with a virus for the past couple of days. When reviewing their lab results, what would you expect to find?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 98
10. Question
A 6-year-old patient treated for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is showing signs of deterioration. Which of the following assessment findings would confirm this suspicion?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 98
11. Question
A change in HCO3– of 10 mEq/L, will change the pH __________ in the same direction?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 98
12. Question
A key component used in the management of both diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) is?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 98
13. Question
A patient being treated for acute pancreatitis has developed significant ascites. They now have diminished breath sounds in the left lower lobe. Current vital signs: BP 116/74, HR 108, RR 36/min, T 98.7°F. Based on the presentation what is suspected?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 98
14. Question
A patient diagnosed with congestive heart failure has received a total of 280mg of Lasix intravenously over the past eight hours. During an assessment of the patient, there is generalized muscle weakness, flat neck veins, and diminished deep tendon reflexes. Which additional assessment finding would help confirm a suspected diagnosis of hyponatremia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 98
15. Question
A patient has received two units of packed red blood cells (PRBCs). The patient’s initial hemoglobin and hematocrit (H&H) was 6 g/dL and 18%. What is their expected H&H after receiving the two units?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 98
16. Question
A patient in initial shock most likely will suffer from which acid-base disorder?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 98
17. Question
A patient involved in a traumatic resuscitation has received five units of packed red blood cells rapidly. What should be of concern in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 98
18. Question
A patient is currently recovering after an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair. Three days later, the patient’s nasogastric tube has been removed and they are eating an advancing diet. They start complaining of excruciating abdominal pain. The patient has a bowel movement that is large and dark red. What is the most likely cause of this pain?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 98
19. Question
A patient is ordered to have constant nasogastric tube suctioning. Based on this, what acid-base derangement is expected?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 98
20. Question
A patient presenting with Beck’s triad is most likely experiencing:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 98
21. Question
A patient presents with a blood glucose of 1087 mg/dL, and negative for ketone production. Their ABG shows a pH of 7.32. Which medication is anticipated to be administered first?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 98
22. Question
A patient underwent abdominal surgery for necrotizing pancreatitis. They have now presented with a diagnosis of a pancreatic fistula as a complication. What metabolic disorder would you most likely suspect to see with this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 98
23. Question
A patient was recently started on enteral feedings at a long-term care facility. They are transferred to the local emergency room due to a change in their level of consciousness. Current lab values are: Na+ 150, BUN 80 mg/dL, serum glucose 870 mg/dL, and serum osmolality 377 mOsm/kg. What is the most likely cause of the abnormal serum osmolality?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 98
24. Question
A patient with a history of hypoparathyroidism is complaining of numbness and tingling around the mouth and in their toes. Which abnormal electrolyte finding is anticipated?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 98
25. Question
A patient experiencing an aplastic sickle cell crisis typically presents with pallor, tachycardia, weakness, and fatigue as well as:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 98
26. Question
A patient’s current hematocrit (Hct) is 58%, and serum sodium (Na+) is 156 mEq/L. What is the most likely cause of these findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 98
27. Question
A pediatric patient is diagnosed with acute cardiac collapse secondary to myocarditis. Upon assessment, the following are noted: BP 72/38, HR 128, RR 34, urine output of 30 mL over the past 3 hours, CVP 12 mmHg, PAP 32/26 mmHg, PCWP 23 mmHg, CI 1.7 L/min/m2. When evaluating this patient’s glomerular filtration rate (GFR), what laboratory value would be best utilized?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 98
28. Question
A post-traumatic injury patient has received six units of packed red blood cells. The patient’s 2,3-DPG is anticipated to change and has what effect on the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 98
29. Question
A shift to the right on the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve is caused by?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 98
30. Question
A patient has a lactate reading of 4.8. What is another finding that would correlate with this?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 98
31. Question
A patient is suffering from septic shock. With regards to the pathophysiology of this disease process, which of the following would NOT be anticipated to be present in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 98
32. Question
After receiving a massive transfusion with packed red blood cells (PRBCs), the patient is experiencing cellular hypoxia secondary to what?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 98
33. Question
All of the following are triggers for sickle cell crisis except?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 98
34. Question
An effect to which of the following would NOT result in a shift on the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 98
35. Question
Beta-blockers are contraindicated in which of the following situations?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 98
36. Question
Bohr effect states?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 98
37. Question
Causes of metabolic alkalosis include all of the following EXCEPT?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 98
38. Question
Classify the pH disorder based on the following ABGs:
pH 7.37, PaCO2 58, HCO3– 23, base deficit -2, PaO2 106
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 98
39. Question
Classify the pH disorder based on the following ABGs:
pH 7.55, PaCO2 30, HCO3– 25, PaO2 56
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 98
40. Question
Dopamine’s alpha-adrenergic effects are related to?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 98
41. Question
Ecchymosis around the umbilicus is called what?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 98
42. Question
Fluid loss in an already dehydrated patient will most critically increase serum levels of which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 98
43. Question
For every 10 mmHg change in PaCO2, the pH will change by ____________ in the opposite direction?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 98
44. Question
Identify the following ABG:
pH 7.28, PaCO2 20, HCO3– 17, PaO2 80, BE -8
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 98
45. Question
Identify the following formula:
CO2 + H2O ↔ H2CO3 ↔ HCO3– + H+
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 98
46. Question
Identify the following pediatric patient’s ABG: pH 7.60, PaCO2 23, HCO3– 35, PaO2 85.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 98
47. Question
Identify the medication with bronchodilating properties.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 98
48. Question
In a patient suffering from metabolic acidosis, what electrolyte becomes elevated due to the acid-base disorder?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 98
49. Question
Labs show the patient’s current lactate level is 6.3 mmol/L. What does this value suggest?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 98
50. Question
Morphine has what other effect on the body besides analgesia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 51 of 98
51. Question
Myoglobinuria, if left untreated, will result in what critical condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 52 of 98
52. Question
Non-cardio selective beta blockers could cause an increased risk of complications in which patient situation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 53 of 98
53. Question
Protracted vomiting typically results in what acid-base imbalance?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 54 of 98
54. Question
Recommended minimum urinary output when caring for an adult patient should be?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 55 of 98
55. Question
The average blood volume for an adult is how many milliliters per kilogram (mL/kg)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 56 of 98
56. Question
The crew is transporting a patient who presented with fatigue, anxiety, and a burning right upper quadrant abdominal pain. They have a significant past medical history of daily IV drug use, hypertension, and hypertriglyceridemia. Upon assessment, there is upper abdominal tenderness and a holosystolic murmur best heard at the lower left sternal border. Current vitals: BP 118/82, HR 118, RR 24, and T 102.5°F. Laboratory studies reveal an elevated white blood cell count, low sodium and chloride and a high sedimentation rate. Which of the following is this patient most at risk for?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 57 of 98
57. Question
The family of a witnessed cardiac arrest victim has been informed that the patient was not successfully resuscitated and has died. The most appropriate communication with the family includes which of the following statements:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 58 of 98
58. Question
The main focus when treating a patient with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 59 of 98
59. Question
The patient is currently receiving a magnesium infusion due to hypomagnesemia (1.2 mEq/L initially). Upon assessment, which finding would alert to stop the infusion immediately?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 60 of 98
60. Question
The primary problem with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 61 of 98
61. Question
The primary treatment in reversing malignant hyperthermia is what medication?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 62 of 98
62. Question
The primary treatment of rapidly evolving disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 63 of 98
63. Question
The sequela of sepsis can lead to multi-organ dysfunction. Which of the following organs is involved first?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 64 of 98
64. Question
The team is transporting a 2-year-old presenting with fever, hyperglycemia, and lethargy for the past three hours. Vital signs are as follows: BP 72/42, HR 146, and RR 32. Upon assessment, there is dry mucous membranes and capillary refill of 4 seconds. Current labs are: K+ 3.0 mEq/L, glucose 485 mg/dL. ABGs: pH 7.1, PaCO2 22, HCO3– 17, PaO2 98. Which of the following types of fluids is most appropriate initially for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 65 of 98
65. Question
The team is transporting a patient who is complaining of severe epigastric pain that is radiating to their back. They have been vomiting consistently for the past 8 hours and cannot get relief from the pain. The patient does admit to greater than moderate use of alcohol on a daily basis but denies smoking or recreational drug use. Upon assessment, there is dry skin and mucous membranes. Upon palpation of the abdomen, there is distention and significant rebound tenderness. Vitals are as follows: BP 92/54, HR 128, RR 24. What is the next best action for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 66 of 98
66. Question
The team is transporting a patient who recently underwent a craniotomy to remove a tumor. They are currently awake, alert, and answering questions appropriately. There are no signs of neurologic deficits. Current vital signs: BP 112/76, HR 88, RR 18, O2 @ 97% on 2 L/min of oxygen via nasal cannula, and blood sugar is 96 mg/dL. Since the craniotomy, they have been urinating approximately 50 mL/hr. Within the last couple of hours, urine output has increased to 350 mL/hr and has a specific gravity of 1.001. What is suspected based on this recent history?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 67 of 98
67. Question
The team is transporting a patient with a diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Current labs and ABGs are as follows:
Na+ 140, Cl– 95, Albumin 3.5, K+ 2.4
pH 6.9, PaCO2 20, HCO3 15, PaO2 80, base deficit -8
The patient has not received any fluid replacement. What is the relationship between pH and K+?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 68 of 98
68. Question
The patient is demonstrating an increase in venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) and a decrease in oxygen consumption (VO2) and pH. What type of shock do you suspect?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 69 of 98
69. Question
What does the following formula represent?
[Na+ – (Cl– + HCO3–) + K+]
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 70 of 98
70. Question
What is the best treatment choice in someone with diabetes insipidus (DI)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 71 of 98
71. Question
What is the drug of choice for a gastrointestinal (GI) bleed?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 72 of 98
72. Question
What is the following equation used to identify?
[1.34 x Hgb x (SaO2)] + PaO2 x 0.003
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 73 of 98
73. Question
What is the leading cause of indirect acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 74 of 98
74. Question
What is the priority when treating respiratory acidosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 75 of 98
75. Question
What is the treatment choice in citrate toxicity?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 76 of 98
76. Question
When administering Albuterol to a 4-year-old, which of the following changes would NOT be anticipated with the administration?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 77 of 98
77. Question
When administering PRBCs, it is anticipated that hemoglobin (Hgb) and hematocrit (Hct) will increase how much with each unit administered?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 78 of 98
78. Question
When assessing a patient’s fractured elbow, damage to the radial and ulnar nerves would present as:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 79 of 98
79. Question
When calculating how PaCO2 affects pH, for every 10 mmHg change in CO2, the pH will change by __________ in the opposite direction?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 80 of 98
80. Question
When treating a pediatric patient with suspected diabetic ketoacidosis, what value can help differentiate the diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) from a hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 81 of 98
81. Question
When treating rhabdomyolysis, giving large amounts of fluid and administering _______________ will help alleviate acidic urine.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 82 of 98
82. Question
Which condition would result in a left shift on the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 83 of 98
83. Question
Which lab finding would be anticipated with diabetes insipidus?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 84 of 98
84. Question
Which medication causes a decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 85 of 98
85. Question
Which of the following ABGs would be suspected in a patient with a diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 86 of 98
86. Question
Which of the following blood gas results would have you preparing to intubate and ventilate the multisystem trauma patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 87 of 98
87. Question
Which of the following can be seen with hypocalcemia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 88 of 98
88. Question
Which of the following conditions would put a patient at the LEAST amount of risk for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 89 of 98
89. Question
Which of the following does not have bronchodilation effects?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 90 of 98
90. Question
Which of the following is not a treatment strategy when dealing with rhabdomyolysis and myoglobinuria?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 91 of 98
91. Question
Which of the following laboratory findings would be expected in a patient with a diagnosis of syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 92 of 98
92. Question
Which of the following medications contains both nonselective beta-adrenergic and alpha1-adrenergic blocking effects?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 93 of 98
93. Question
Which type of medication blocks the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) system to help with heart failure?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 94 of 98
94. Question
With a diagnosis of diabetes insipidus (DI), what lab findings would be anticipated?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 95 of 98
95. Question
With regards to the pathophysiology of sepsis, which of the following would be anticipated in a patient with a diagnosis of sepsis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 96 of 98
96. Question
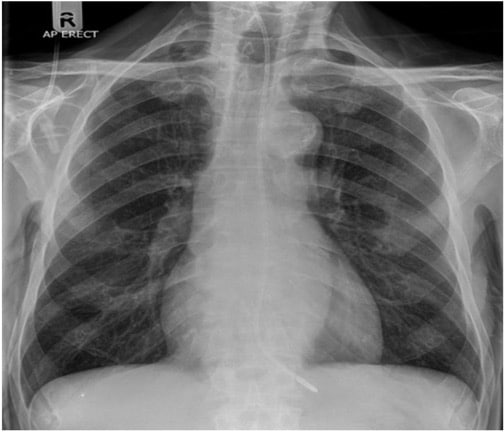
You are transporting a patient with a nasogastric tube (NGT) that was placed by the transferring facility. You look at the x-ray to confirm placement and note the following:
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 97 of 98
97. Question
You are transporting an intoxicated patient who was involved in a motor vehicle collision and sustained a closed femur fracture. Which types of hypoxia-related problems may occur in flight?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 98 of 98
98. Question
____________ is a drug that has potent alpha effects and is used to increase systemic vascular resistance (SVR) in profound vasodilatory redistributive shock states such as sepsis and neurogenic shock.
CorrectIncorrect
